Marine Fuel Injection
Who invented Fuel injection and why?
The first use of direct petrol injection was in 1925 on the Hasselman engine invented by Swedish engineer Jonas Hasselman. This was a hybrid engine designed to run on both Petrol and Diesel, it was used in busses and heavy trucks in the 1920-1930s. Gasoline injection systems were designed during world war 2 for aircraft because of its greater imunity to wildly changing g-forces.
How does a single and multi injection system work?
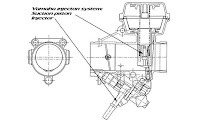 Single Injection system - This is when a single injector is fitted just behind the throttle body. As the air passes the throttle butterfly the injector sprays a mist of fuel which mixes with the air as it is drawn into the combustion chamber. The MAF, MAP, MAT sensors all assist the ECU in maintaining a steady fuel mixture.
Single Injection system - This is when a single injector is fitted just behind the throttle body. As the air passes the throttle butterfly the injector sprays a mist of fuel which mixes with the air as it is drawn into the combustion chamber. The MAF, MAP, MAT sensors all assist the ECU in maintaining a steady fuel mixture.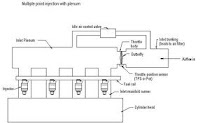 Multi Injection system - This refers to a system were the fuel is injected at multiple points. Usually there will be an injector located at the bottom of the inlet manifold, just above the intake valve on each cyclinder. This system produces a better Air/fuel mix and allows the inlet manifold to be designed to maximise air flow.
Multi Injection system - This refers to a system were the fuel is injected at multiple points. Usually there will be an injector located at the bottom of the inlet manifold, just above the intake valve on each cyclinder. This system produces a better Air/fuel mix and allows the inlet manifold to be designed to maximise air flow.What does EFI stand for?
EFI stands for Electronic Fuel Injection. This is a name that refers to a Petrol internal combustion engine that is electronnicaly controled and is fuel injected as apposed to Carburetted.
ECU stands for Electronnic Control Unit or Engine Control Unit. This is like the brain of the engine. Signals from various engine sensors are sent to this unit, the ECU then sends signals to components such as the injectors or intake butterflies. Through operations such as that the ECU maintains control of the engine.
(MAF) Mass Air Flow sensor?
This is the sensor that is used to measure the amont of air entering the engine. The information gathered by this sensor is sent to the ECU and allows it to adjust the fuel delivery as necessary. Two common sensors are the Hotwire sensor and Vane meter. These sensors to need input from additional sensors to be accurate. Other less common sensors are the Coldwire sensor, Karmnan Vortex sensor and the Membrane sensor.

Hotwire Sensor
The hot wire sensor works by passing a current through a wire suspended in the air intake. As the wire heats up the electrical ressistance increases, limiting electrical current. As air passes over the wire the heat reduces allowing more current to pass throught the circute. These changes in current are converted into voltage which is sent to the ECU.
Vane Sensor
The Vane Airflow sensor is a spring loaded airflap that is attached to a variable resistor. As air flow increases the flap opens and the resistor moves. As the angle of the resistor varys so does the voltage being sent to the ECU. Some draw backs such as:
- Can restrict airflow
- Need to be oreinted in respect to gravity
- Electrical and Mechanical contacts can wear
(MAT) Manifold Air Temperature sensor?
This sensor is a thermistor, a resistor that reduces resistance with temperature increase. It is screwed into the intake manifold to measure manifold air temperature and relay it to the ECU.
(MAP) Manifold Absolute Pressure sensor?
This sensor measures manifold pressure. It is responsive to vacuum and barometric pressure. Air/Fuel ratio, Ignition timing an Idle speed can all be modified by the ECU as a result of the MAP sensors signal.
This sensor is used to measure the position of the throttle butterfly within the throttle body. This sensor is usually located on butterfly spindle and directly monitor the valve position. The sensor is a variable ressistor therefore will send a different signal depending on throttle position.
Oxygen/Lambda sensor?
This sensor is used to measure the Oxygen within the exhaust fumes. By determining the Oxygen level we are able to establish in real time if the engine is running rich or lean. This also helps with emissions.

Engine Temperature sensor?

Engine Temperature sensor?
The engine temperature sensor is located in the engine coolant. Measuring the temperature of the coolant is a good way to determine the engine temperature.
Cam & Crankshaft Position sensors?
This sensor is used to determine the (RPM) rotational speed at which the Cam/Crankshaft is moving and the Cam/Crankshaft position. This sensor will consist of a rotating part, generaly a disc with magnet, and a static part. The actual sensor. This sensor is not always located directly on the Cam/Crankshaft, it can also be run off a belt or gear. The signal from both the Cam Position sensor and the Crank Position sensor alow the ECU to adjust the ignition timing, idle annd acceleration.
Idle air supply.
When the engine is idleing the throttle butterfly is closed and allows very little air past. So air passages are provided that bypass the throttle valve to allow air into the intake during idle. These air passages can sometimes be adjusted with a screw on the throttle body.
The throttle body is the housing that holds the throttle assembly and sensors. This assembly controls the air flow to the engine and responds to the accelerator pedal.
What is the Plenum chamber?
The Plenum chamber is used to distribute air flow between cylinders. Air flows through the throttle body into the plenum chamber (often moulded and surfaced for better flow and distribution) then through the intake manifold, mixing with the fuel just before entering the cylinder.
What are Injectors?
Injectors are the final piece to the fuel system puzzle. Located in the intake manifold just about the intake valve, the injectors deliver a specific amount of fuel to each cylinder. Signals from the ECU tell the injectors when to open and how long to open for.
What is a Fuel pressure regulator?
This is a metal housed, spring-loaded diapragm used to regulate the pressure in the fuel system. Regulating pressure is usually around 250kpa and is set durinng manufacture. Pressure is determined by strength of the spring. the chamber above the diaphragm is connected to the intake manifold and so subject to vacuum. When excess pressure builds up the diaphragm lifts the valve and returns extra fuel to the fuel tank.



What is a Fuel rail?
A fuel rail runs along the engine and delivers fuel directly to the injectors. Fuel is delivered to the fuel rail via fuel lines from the fuel pump. The fuel rail is kept at pressure and regulated by the pressure regulator.
References
Ed May Vol 1
Ed May Vol 2





Great effort again, well worth reading.
ReplyDelete