Marine Trailers
Single Axle - As they are generaly small, these are easy to manouver, light and low maintenece. These are the most common type of trailer and do not have a braking system. They have a SWL of 2000kgs.

Tandem Axle - 1 axle and 2 extra tyres make for a much smoother ride. Combine that with a braking system and you increase the SWL greatly(Will vary depending on braking system). Maintenece does increase as there is now a braking system and extra fittings.
Triple Axle - Generally only used in special circumstances, such as when transporting for repair. These trailers have huge SWL, with this comes the extra maintenece of 3 Axles and fittings to suit. Ranging in size these trailers can be towed by a 4-wheel drive or truck.
Trailer Materials
Mild Steel - Steel is generaly an Alloy of Iron and Cabon, and can have other elements added to it to give it desired attributes. Modern day Mild Steel contains low carbon, usually less than 0.8%, and practicly no slag. Mild Steel is strong and able to with stand an impact with out shattering. Steel is heavy and will need to be treated to prevent oxidization in salt water. Painted steal is good for fresh water.
Galvanized Steel - Galvanized Steel has the same characteristics as mild steel, but has been coated in a Zinc layer for protection againsed corrsion. Zinc is easier and cheaper than using other metallic coatings such an Chromium, Aluminium or Nickel. In a process called 'Hot Dipping' the Mild steel frame is dipped in Acid to remove dirt & grease, then dryed and dipped into a pool of molten Zinc. Especially good for Sea water boats.
Aluminium - Aluminium is the most abundant metallic elment in the Earths crust. It is a strong electropositive metal and is extremely reactive. When exposed to air Aluminium becomes covered in a tough, transperent layer of Aluminium oxide. this layer serves as protection from corrosion. Aluminium weighs less than a third of the same volume of steel, and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. Can be expensive but this material needs no further protection.
Trailer Design & Construction
Design
A-Frame - This is a basic design but distributes weight well across the trailer.
A-Frame - This is a basic design but distributes weight well across the trailer.
Pole Tongue - This design can accomodates a tilting deck and is usually for lighter boats.Blogs
Construction
-Once you have your material you will focus on design. Below are a few forms of frame constructruction.
- The best form of construction in my opinion would be either Box or Pipe tubeing. This design form has a good strength and can protect wires from impact and sun exposure.
- If using I-beams or Channel-beams it is recommended that you use either Galvanized or Mild steel as Aluminium would not be strong enough.
- If using I-beams or Channel-beams it is recommended that you use either Galvanized or Mild steel as Aluminium would not be strong enough.
WOF Regulation
Width - The maximum width of a trailer is 2.5m and any trailer that is wider than 1.8m must have foward facing side lamps.
Rear overhang - The load must not overhang more than 4m from the rear axle.
Foward disance - The distance from the rear axle to the tow coupling must not exceed 8.5m.
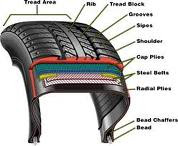
Tyres - Must be a minimum of 1.5mm tread acros 3/4 of the tyre.
Suspension & Weight Capabilities
Leaf spring suspension- Leaf springs are most commonly used. they are able to withstand varying loads depending how many leaves in the spring. There are a few variations of the leaf spring.

Coil Spring suspension - Coil springs are able to withstand heavy loads. Combine with shock absorber to smooth load.
Torsion suspension - A torsion suspesion is as follows.
Disk type System - A Disc type braking system would be the most common type of system in modern trailers. Disk brakes work as hydrolic fuild is pushed against a piston clamping the brake pad against the rotor. This brake system can be upgraded to provide more stopping power by increasing the number of pistons per caliper.


Drum type System - Drum type brakes are used on smaller trailers. These brakes work when the hydrolic cylinder pushes the brake shoes outward toward the inside of the brake drum, slowing the rotation as friction builds. Drum brakes can be problematic in the marine industry as water can get into the drum and mixes with the brake dust, this then turns to a paste and when dry can cause the brakes to seize.
Hydrolic Brakes - Both disk and drum brakes can be hydrolic. Hydrolic trailer brakes are controlled by the Master cylinder on the tow coupling as below.
Cable Brakes - Both disk and drum brakes can be Cable controlled. A cable is attached to the caliper in a way that when pulled tight a clamping force is exerted. this cable is controlled by a handle on the tow coulping, as left, and can be locked into position.
Hydrolic Brakes - Both disk and drum brakes can be hydrolic. Hydrolic trailer brakes are controlled by the Master cylinder on the tow coupling as below.

Cable Brakes - Both disk and drum brakes can be Cable controlled. A cable is attached to the caliper in a way that when pulled tight a clamping force is exerted. this cable is controlled by a handle on the tow coulping, as left, and can be locked into position.
A trailers SWL is governed by the rating of the tow coupling.
Rims & Tyres
Generaly 13-14" Steel or Alloy rims. These can be replaced with mag wheels if desired.
Tyres can range in width, profile, weight bearing capacity & purpose. Choose a wider tyre for a more stable load. Tyres have different speed ratings also.
Its important that when choosing a tyre that the tyre fitted is built for trailer use. As trailer tyres have stronger side wall to withstand larger weight loads and prevent blow outs.
Lighting & Fittings
Tail lightsUsealed bulb lights - Unsealed bulb lights are common on older trailers. When a trailer enters the water the lights may become submerged, as this unit is not a sealed unit it will corrode easily and will need to be replaced.
Sealed L.E.D lights - (Light Emitting Diode) Sealed L.E.D lights would be the best for most applications. As the unit is sealed the possiblity of corrosion is very low unless the casing has been damaged in some way. L.E.D lights are very energy efficent. The downside to them is that if a couple of the tiny bulbs blow then the whole unit needs to be replaced.
- You may like to fix you light board high on your trailer similar to this picture, to reduce corrosion.
Rollers
Keel roller - This roller is designed to protect the keel of your boat during transportation. The keel roller is prefered as it is designed to roll as the boat is loaded, reducing friction.

Keel block - As with the keel roller this is designed to protect the keel of your boat during transportation. Made from rubber this design is often disliked due to the friction it causes when loading the boat.
Ribbed roller - You will usually find many ribbed rollers on a trailer. They are used to help guide the boat onto the trailer when loading, and to spread the load of the boat evenly across is hull. See single axle trailer pic.
Stop block - This is a rubber stop that is located at the front of the trailer and allows the winch to pull the boat up tight againsted the front of the trailer.
Winch - The winch should be able to pull a load equal to at least half of the gross weight of the boat, motor and cargo. Be sure to check for corrosion and damage before use to reduce risk of damaging boat. Electric winches are also available.
References
http://www.google.com/
http://www.boatdesign.com/
http://www.nzta.govt.nz/
Encarter 2004